
Cartoview Core Installation | Ubuntu
Introduction
This guide describes how to install and configure a fresh setup of Cartoview to run it in DEBUG mode (also known as DEVELOPMENT mode) on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS 64-bit clean environment (Desktop or Server).
This part of the documentation describes installation of Cartoview-1.33.2 which comes with GeoNode-3.3.2.post1 and GeoServer-2.19.6.
Warning
Those guides are not meant to be used on a production system. Instead, you can follow the Docker guide.
Note
All examples use shell commands that you must enter on a local terminal or a remote shell.
If you plan to customize Cartoview & GeoNode user interface components to your needs, it's recommended to use cartoview-project. Check the available cartoview-project guide.
Installation Requirements
Install all system packages that are needed for Cartoview setup.
# Update and Upgrade system packages
sudo apt update -y; sudo apt upgrade -y;
# Install required packages
sudo apt install -y build-essential gdal-bin \
python3.8-dev python3.8-venv virtualenvwrapper \
libxml2 libxml2-dev gettext \
libxslt1-dev libjpeg-dev libpng-dev libpq-dev libgdal-dev \
software-properties-common build-essential \
gcc zlib1g-dev libgeos-dev libproj-dev
# Install Openjdk
sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk-headless default-jdk-headless -y
sudo update-java-alternatives --jre-headless --jre --set java-1.8.0-openjdk-amd64
# Verify GDAL version
gdalinfo --version
$> GDAL 3.3.2, released 2021/09/01
# Verify Python version
python3.8 --version
$> Python 3.8.10
which python3.8
$> /usr/bin/python3.8
# Verify Java version
java -version
$> openjdk version "1.8.0_292"
$> OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_292-8u292-b10-0ubuntu2~20.04-b10)
$> OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.292-b10, mixed mode)
# Cleanup the packages
sudo apt update -y; sudo apt upgrade -y; sudo apt autoremove --purge
Note
Those steps must be done only if you don’t have the DB already installed on your system.
# Ubuntu 20.04 (focal)
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb https://apt.postgresql.org/pub/repos/apt/ `lsb_release -cs`-pgdg main" >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pgdg.list'
sudo wget --no-check-certificate --quiet -O - https://www.postgresql.org/media/keys/ACCC4CF8.asc | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt update -y; sudo apt install -y postgresql-13 postgresql-13-postgis-3 postgresql-13-postgis-3-scripts postgresql-13 postgresql-client-13
Note
Optional | You can also install pgAdmin ( A PostgreSQL GUI tool using ): sudo apt-get install pgadmin4
Note
For more Information, visit PostgreSQL download page.
Database Configuration
In this section we are going to configure PostgreSQL interactive terminal to create the databases.
Connect to a running database instance
You must connect to PostgresSQL as the postgres user, PostgresSQL default superuser.
sudo -i -u postgres
Set the postgres user password to postgis.
psql
This will open PostgreSQL interactive terminal. Set the postgres user password to postgis:
\password
Exit the PostgreSQL prompt by typing:
\q
Update Access Policies for local connections
Update access policies for local connections in the file pg_hba.conf to be able to connect to the database properly.
sudo nano /etc/postgresql/13/main/pg_hba.conf
Scroll down to the bottom of the document. We want to make local connection trusted for the default user.
Make sure your configuration looks like the one below.
...
# DO NOT DISABLE!
# If you change this first entry you will need to make sure that the
# database superuser can access the database using some other method.
# Noninteractive access to all databases is required during automatic
# maintenance (custom daily cronjobs, replication, and similar tasks).
#
# Database administrative login by Unix domain socket
local all postgres trust
# TYPE DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD
# "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only
local all all md5
# IPv4 local connections:
host all all 127.0.0.1/32 md5
# IPv6 local connections:
host all all ::1/128 md5
# Allow replication connections from localhost, by a user with the
# replication privilege.
local replication all peer
host replication all 127.0.0.1/32 md5
host replication all ::1/128 md5
Warning
If your PostgreSQL database resides on a separate/remote machine, you’ll have to allow remote access to the databases in the
/etc/postgresql/13/main/pg_hba.conf to the postgres user and tell PostgreSQL to accept non-local connections in your
/etc/postgresql/13/main/postgresql conf file.
Restart PostgreSQL to make the change effective and be able to connect to PostgreSQL successfully.
sudo service postgresql restart
Create Cartoview Databases
Create two new databases cartoview and cartoview_datastore.
createdb cartoview
createdb cartoview_datastore
Add PostGIS extension to the created databases to deal with the geographic objects.
For cartoview database:
psql cartoview # To be executed at ubuntu terminal
CREATE EXTENSION postgis; # To be executed at psql terminal
Exit the PostgreSQL terminal with \q
For cartoview_datastore database:
psql cartoview_datastore # To be executed at ubuntu terminal
CREATE EXTENSION postgis; # To be executed at psql terminal
Note
The previous step must be done for the two databases, cartoview and cartoview_datastore.
You can now log out back to your usual user (other than postgres) by just typing exit.
Cartoview Installation
Create a Python Virtual Environment
Let's make a directory called cartoview_service (You can name it whatever you prefer) that will contain two folders, python virtual environment and cartoview.
mkdir cartoview_service
cd cartoview_service
Create and activate the python virtual environment, we will name it cartoview_venv.
Note
You can name it whatever you prefer, but bear in mind changing every cartoview_venv in the commands below with the name you want for your virtual environment.
# Create the Cartoview Virtual Environment (first time only)
mkvirtualenv --python=python3.8 cartoview_venv
Note
- You would notice how your prompt is now prefixed with the name of the virtual environment,
cartoview_venvin our case. This indicates that your virtualenv is active. - From now on, each command must be executed while the virtual environment is activated.
Cartoview Libraries Installation
Warning
Make sure you're inside cartoview_service directory and the cartoview_venv is still activated.
Download Cartoview 1.33.2 version by cloning the repository and checkout the release tag.
git clone -b v1.33.2 https://github.com/cartologic/cartoview.git
This will create a folder called cartoview inside cartoview_service directory.
Cartoview Dependencies Installation
Navigate to cartoview directory and install cartoview dependencies.
cd cartoview
pip install -e .
pip install pygdal=="`gdal-config --version`.*"
Warning
Make sure you got the dot . when you copy the previous command.
Add Cartoview Environment Variables
Cartoview requires adding some environment variables while running it or executing commands through terminal.
It's recommended to use PyCharm which is a powerful python IDE that has a lot of features to offer.
Create a new PyCharm configuration and add the following environment variables accordingly.
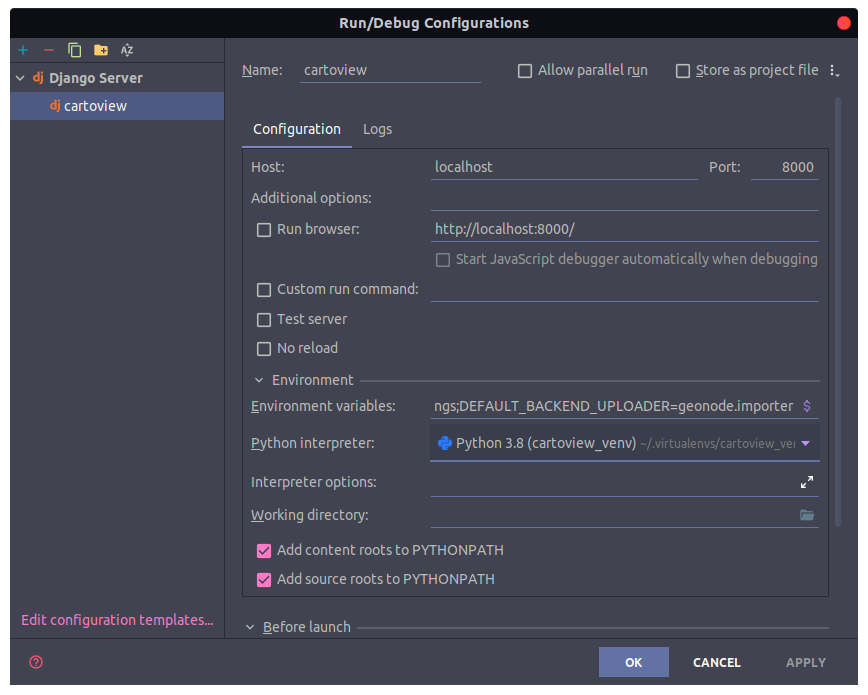
DATABASE_URL=postgis://postgres:postgis@localhost:5432/cartoview
DATASTORE_DATABASE_URL=postgis://postgres:postgis@localhost:5432/cartoview_datastore
ALLOWED_HOSTS=['*']
DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE=cartoview.settings
DEFAULT_BACKEND_UPLOADER=geonode.importer
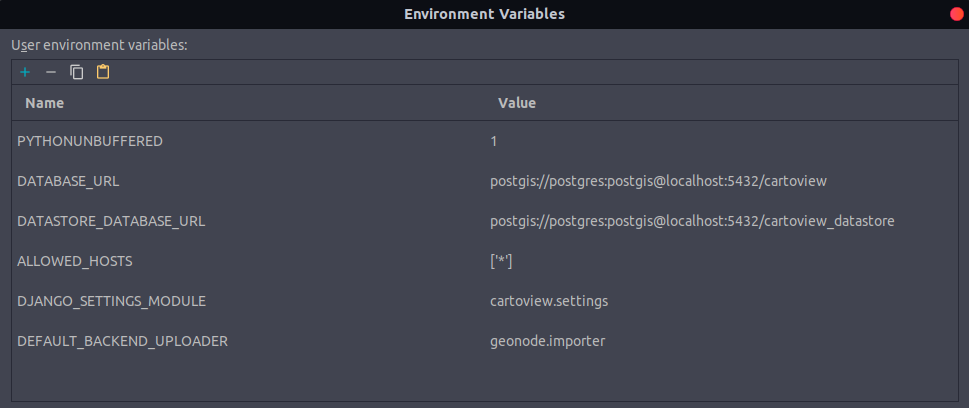
It's required to add them also to the terminal configuration.
But the following variables only.
DATABASE_URL=postgis://postgres:postgis@localhost:5432/cartoview
DATASTORE_DATABASE_URL=postgis://postgres:postgis@localhost:5432/cartoview_datastore
ALLOWED_HOSTS=['*']
Migrate & Load default data
Inside cartoview folder, run the below commands to migrate and load Cartoview data.
Warning
- Make sure the virtual environment is still activated (If you see its name prefixed your prompt, you're good to go).
- Make sure to add the above environment variables to the terminal so that the following commands run smoothly.
Migrate the data.
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
Load default User.
python manage.py loaddata sample_admin.json
Load default oauth apps so that you will be able to authenticate with defined external server.
python manage.py loaddata default_oauth_apps.json
Load default cartoview appstore data.
python manage.py loaddata app_stores.json
Load default cartoview initial data.
python manage.py loaddata initial_data.json
Collect static files.
python manage.py collectstatic --noinput
In order to make the ArcGIS Importer app work properly, generate API keys.
python manage.py backfill_api_keys
Test Development Server
Check if Cartoview is working as expected.
python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000
Open a browser and check if cartoview is running at localhost:8000.
You should be able to successfully log with the default admin user (admin / admin) and start using it right away.
Now we have Cartoview up and running. The last thing we need to do, is to install and configure GeoServer.
GeoServer Installation
Cartoview comes with a pre-configured GeoServer available by GeoNode. So it can be installed with Paver commands.
If you check the pavement.py file, you can see multiple created tasks like, setup_geoserver, start_geoserver, and stop_geoserver.
Warning
Make sure the virtual environment is still activated (If you see its name prefixed your prompt, you're good to go).
Run the task called setup_geoserver to download a customized version of GeoServer WAR file (provided by GeoNode) and setup jetty.
Note
- Jetty provides a web server and servlet container. It's used to host GeoServer.
- The file called
dev_config.ymlholds the download URL for GeoServer and Jetty.
paver setup_geoserver
This will create two folders, the first one called downloaded, it contains the downloaded required files and geoserver which contains all the files related to GeoServer.
Start GeoServer
Run the task called start_geoserver to launch jetty on port 8080 and start GeoServer.
Warning
Make sure nothing is running on port 8080.
paver start_geoserver
GeoServer is now available and running at http://localhost:8080/geoserver/.
Make sure you're logged in with admin/admin in Cartoview at http://localhost:8000/ then navigate to
http://localhost:8080/geoserver/ and click on the GeoNode button to use the pre-configured authentication between GeoNode and GeoServer.
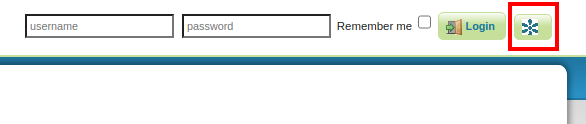
Note
You can also log in with the default GeoServer credentials admin/geoserver, but using GeoNode button is easier.
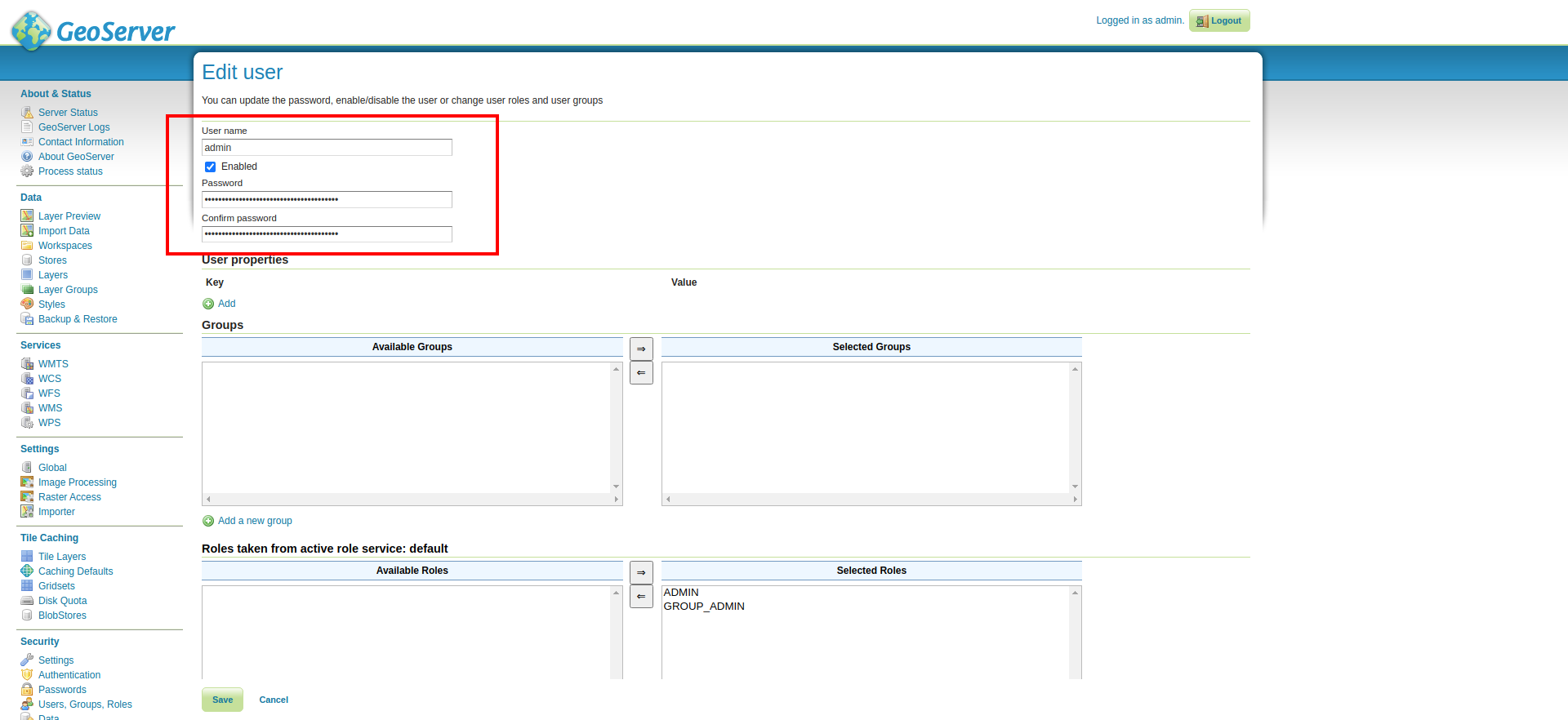
You can change the admin password by navigating to Security > Users, Groups, and Roles. Select Users/Groups tab, select admin user, and you can now update the password as you want.
Stop GeoServer
GeoServer can be stopped by running the task stop_geoserver.
paver stop_geoserver
Note
When GeoServer is stopped, the jetty server got down also but all the uploaded data (e.g. layers) is saved in the folder called geoserver in cartoview directory.
Post-Installation Notes
Congratulations! Cartoview is now installed successfully.
You can upload layers, create maps, and install Cartoview apps to visualize these maps.
Once Cartoview is installed, You can navigate to the apps to check and install all available apps from the App Store.
After installing any app, you may need to restart the running django server if you can't see your app in /cv_apps.